Step 2: How to Change DNS Settings
The best place to change the DNS settings is on your router, as that way any device that connects to the router will automatically benefit from the DNS filtering. Unfortunately some ISPs do not permit its customers to change the DNS settings on their routers. In such an instance the only option available is to change the DNS settings on each device that connects to the router, or to try the wifi hotspot workaround described later on.
1. Firstly, see if you can change the DNS settings on your router (simply type in the ISP provider plus the router model into Google and see what this turns up). It is usually necessary to log into the router to make changes to any of the settings, here again Google will provide you with the necessary information on how to do this.
2. If it is not possible to change the router DNS settings then you will need to configure each internet-enabled device individually. Type in a search string into Google along the lines of “change DNS settings Windows 10” (or whatever the device happens to be) and follow the steps outlined.
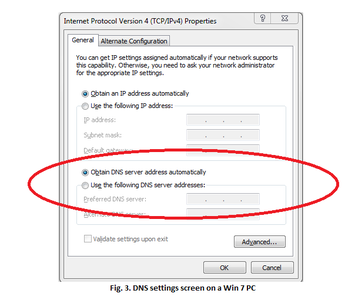
3. You may need to navigate through a variety of different sub-menus within the Settings menu to get to the one where you can access the DNS settings for your device. Fig. 3. shows what the relevant screens for changing the DNS settings look like on a Windows 7 PC. Although the screen for your device may look radically different to the one shown you should be able to find a section on it which deals with DNS settings (see the section highlighted in the red ring in the figures below). In some instances there may be an option to allow the DNS settings to be selected automatically, or else there may be some default value displayed.
4. Click on the option to allow you to manually define the DNS server addresses, and then enter the appropriate details for the CleanBrowsing Family IP filter addresses into the relevant fields. Some newer hardware may have options for both IPv4 and IPv6 settings, but the majority of hardware will only have the option to use IPv4 settings. If your device only has one input field for DNS server settings then you can enter both server addresses by placing a comma between the addresses.
Server 1: IPv4 settings — 185.228.168.168/ IPv6 settings — 2a0d:2a00:1::
Server 2: IPv4 settings — 185.228.168.169 / IPv6 settings — 2a0d:2a00:2::
5. Save the settings and then exit from the Settings menu. That’s it!
Каковы причины утечки DNS
Существует несколько причин утечки DNS:
Проблема в конфигурации сети
При подключении к Интернету убедитесь, что вы используете стабильное соединение. Часто случается, что соединение прерывается на несколько секунд до того, как будет установлено новое соединение. Это приводит к изменению IP-адреса. Когда это изменение произойдёт, вы можете подключиться к DNS-серверу вашего интернет-провайдера, даже если вы используете VPN. Хакеры могут проникнуть в соединение, поскольку ваша VPN не будет работать из-за внезапного изменения IP-адреса и раскрыть вашу информацию.
Утечки IPv6
Большинство IP-адресов состоят из четырех наборов трёхзначных кодов, например 111.111.111.111; это называется IPv4-адресом. Однако, Интернет медленно переходит в фазу IPv6, когда IP-адреса состоят из восьми наборов по 4 кода, которые также могут включать буквы.
В большинстве случаев, если вы отправляете запрос IPv6 на свой DNS-сервер для веб-сайта, у которого всё ещё есть адрес IPv4, в таком случае безопасность соединения может быть нарушена. Даже в случае соединения VPN запрос IPv6 обходит шифрование VPN, если VPN явно не поддерживает безопасность соединения IPv6.
Прозрачные DNS-прокси
VPN туннелирует ваше соединение через сторонний сервер, прежде чем достигнет DNS-серверов вашего интернет-провайдера, чтобы замаскировать ваш IP-адрес. Это также удерживает интернет-провайдеров от сбора и мониторинга ваших данных или действий в Интернете.
Иногда интернет-провайдеры используют отдельный или прокси-сервер для повторного перенаправления ваших запросов и веб-трафика на свои серверы – таким образом, интернет-провайдеры во многих случаях «заставляют» утечки DNS собирать информацию о пользователях.
Функция Windows «Smart Multi-Homed Name Resolution»
«Smart Multi-Homed Name Resolution» – это функция, представленная Windows версии 8.0. Эта функция позволяет подключаться к другим нестандартным серверам, отличным от того, который принадлежит соответствующим интернет-провайдерам, если серверы интернет-провайдеров перестают отвечать.
В Windows 10 эта функция позволяет принимать ответы на запросы DNS от любого самого быстрого доступного сервера. Так как это позволяет читать IP-адреса пользователей разными серверами, это может вызывать серьёзные проблемы, связанные с утечками DNS.
Проблема Teredo
Teredo – это технология, разработанная Mircosoft, которая позволяет пользователям находить IPv6-совместимые соединения с веб-сайтами и плавно переходить с IPv4 на IPv6. В этой технологии ваш запрос IPv4 туннелируется таким образом, что адреса веб-сайтов IPv4 выбирают их. Однако, этот процесс может обойти процесс туннелирования VPN и раскрыть ваш IP-адрес, что приведёт к утечке DNS.
Скрещивание с TLS
Положительный момент в том, что Stubby допускает конфигурации с использованием нескольких служб на основе DNS по TLS. Файл конфигурации на YAML позволяет настроить несколько служб IPv4 и IPv6 и включает в себя настройки для SURFNet, Quad9 и других сервисов. Однако реализация YAML, используемая Stubby, чувствительна к пробелам, поэтому будьте осторожны при добавлении новой службы (например, Cloudflare). Сначала я использовал табы — и всё поломал.
— address_data: 1.1.1.1
tls_auth_name: «cloudflare-dns.com»
tls_pubkey_pinset:
— digest: «sha256»
value: yioEpqeR4WtDwE9YxNVnCEkTxIjx6EEIwFSQW+lJsbc=
— address_data: 1.0.0.1
tls_auth_name: «cloudflare-dns.com»
tls_pubkey_pinset:
— digest: «sha256»
value: yioEpqeR4WtDwE9YxNVnCEkTxIjx6EEIwFSQW+lJsbc=
После установления TCP-соединения клиента с сервером через порт 853 сервер представляет свой сертификат, а клиент сверяет его с хэшем. Если всё в порядке, то клиент и сервер производят рукопожатие TLS, обмениваются ключами и запускают зашифрованный сеанс связи. С этого момента данные в зашифрованной сессии следуют тем же правилам, что и в DNS по TCP.
После успешного запуска Stubby я изменил сетевые настройки сети DNS, чтобы направлять запросы на 127.0.0.1 (localhost). Сниффер Wireshark хорошо показывает этот момент переключения, когда трафик DNS становится невидимым.
Хотя DNS по TLS может работать как DNS по TCP, но шифрование TLS немного сказывается на производительности. Запросы dig к Cloudflare через Stubby у меня выполнялись в среднем около 50 миллисекунд (у вас результат может отличаться), в то время как простые DNS-запросы к Cloudflare получают ответ менее чем за 20 мс.
Здесь тоже имеется проблема с управлением сертификатами. Если провайдер удалит сертификат и начнёт использовать новый, то в настоящее время нет чистого способа обновления данных SPKI на клиентах, кроме вырезания старого и вставки нового сертификата в файл конфигурации. Прежде чем с этим разберутся, было бы полезно использовать какую-то схему управления ключами. И поскольку сервис работает на редком порту 853, то с высокой вероятностью DNS по TLS могут заблокировать на файрволе.
Но это не проблема для лидера нашего хит-парада — DNS по HTTPS. Он проходит через большинство файрволов, словно тех не существует.
 Google и Cloudflare, похоже, одинаково видят будущее зашифрованного DNS
Google и Cloudflare, похоже, одинаково видят будущее зашифрованного DNS
DoHодим до сути
Здесь резонно задаться вопросом: а в чем вообще тут может быть проблема? Чем больше безопасности, тем лучше, разве не так?
Ответ на этот вопрос лежит в нюансах выбранных решений, их сильных и слабых сторонах. А именно в том, как новая технология взаимодействует с разными участниками системы DNS, кого из них ее разработчики считают условно заслуживающими доверия, а кого — источниками угрозы. И речь сейчас даже не о хакерах-злоумышленниках, имеющих откровенно преступные цели.
Речь о том, что между пользовательским устройством и конечным сайтом находятся посредники. Администратор сети, файрвол, провайдер интернета — все они могут в своих интересах взаимодействовать с системой DNS, задавая своим резолверам имен DNS настройки того, какие запросы отслеживать, блокировать, модифицировать. Так можно встраивать рекламу, отсекать вредоносный контент, не пускать на определенные ресурсы…
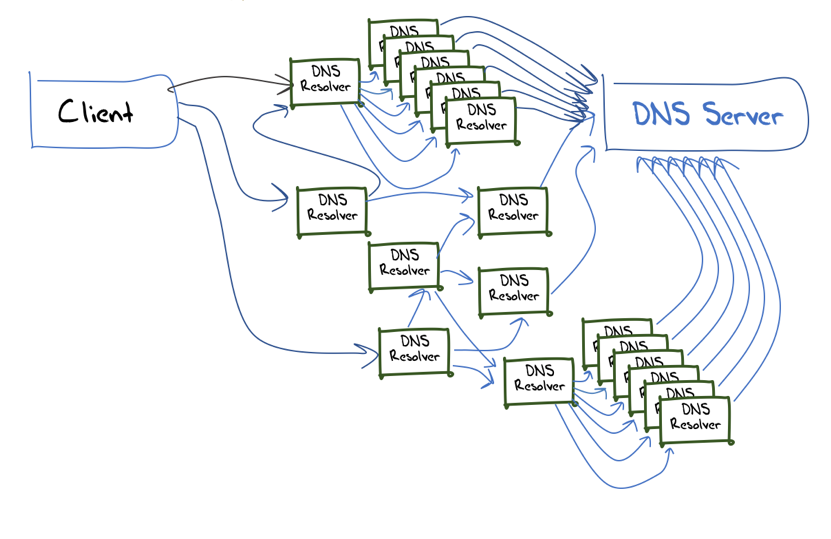 Путь запроса от клиента до сервера может проходить через множество резолверов
Путь запроса от клиента до сервера может проходить через множество резолверов
DoT, работая через TLS с его системой сертификатов доверия, точно так же нуждается в DNS-резолвере, которому он сможет доверять. Присутствует гибкая возможность настройки списка доверенных резолверов, возможность централизованного изменения настроек в предварительно доверенной (например, корпоративной) среде, а также возможность переключаться обратно на базовый DNS, если с новой версией возникнут проблемы.
Поскольку для DoT используется новый, выделенный порт, возможно заметить передаваемый трафик и наблюдать за его объемами, шифрование этому никак не помешает. При желании можно даже заблокировать его вовсе.
В общем, DoT нужно грамотно настроить, но зато он содержит некоторые крайне полезные для системных администраторов и сетевых инженеров функции. Поэтому многие из профессионалов и хвалят за это DoT.
С DoH история другая. Эта технология разрабатывалась с расчетом на пользовательские приложения, а именно — браузеры. Это ключевая деталь во всей этой истории. Означает она вот что. При использовании DoH весь трафик, который не относится к браузерам, идет через базовый DNS, но браузерный трафик при этом обходит любые настройки DNS — на уровне операционной системы, локальной сети, провайдера — и, минуя промежуточные этапы, по HTTPS попадает сразу к поддерживающему DoH резолверу DNS.
И к этой схеме есть ряд серьезных вопросов.
Block Adult Websites on Windows 11/10 using DNS Services
These websites offer IP, which acts as a Filter on top of DNS. Whenever a website is accessed, they check if it has been marked for any adult activities. If yes, access to the website is blocked. You can thus block inappropriate adult sites on Windows 10 using these DNS Services:
- Open DNS Family Shield
- Clean Browsing
- Cloudflare 1.1.1.1 for Families
- NeuStar Family Secure DNS
- DNS for Family
- Yandex
To configure all of them, you need to configure IP addresses in the DNS field of the adapter or router. So you will need to access to Router or computer where you can enter them. When doing it on the computer, you will need admin privileges.
They can also be configured on smartphones to make sure kids don’t get access even when they are using mobile data. Android gives the option to configure IP settings under the advanced section. The configuration may vary from phone to phone.
Read: Why visiting adult websites could affect your security and privacy?
1] Open DNS Family Shield
OpenDNS nameservers are built to make sure they filter out all the adult content, and if someone tries to access them, it gets blocked. OpenDNS FamilyShield nameservers are:
- 208.67.222.123
- 208.67.220.123
If the Welcome Page or test page shows an error, restart the router and the computer. It will make sure there is no caching of DNS IP anywhere.
Read: How to block websites in Chrome or Firefox
2] Clean Browsing
Clean Browsing offer three types of filters—Security, Adult, and Family. While Adult Filter only blocks Adult domains, Search Engines set to safe mode, and Security Filter, Family goes one step ahead. It sets up VPNs; Mixed Adult Content blocked, and Youtube to safe mode along with the Adult filter.
- Security Filter: 185.228.168.9: Malicious domains blocked (phishing, malware).
- Adult Filter: 185.228.168.10: Adult domains blocked; Search Engines set to safe mode; +Security Filter
- Family Filter: 185.228.168.168: Proxies, VPNs & Mixed Adult Content blocked; Youtube to safe mode; +Adult Filter
They offer three content filters via Pv4 and IPv6 through standard port 53 and 5353. DNS over TLS is available over port 853 and DNScrypt over port 8443.
Firefox users can also turn on Adult Filter on the New Tab Page.
TIP: This post shows how to block a website in Microsoft Edge using three methods.
3] Cloudflare 1.1.1.1 for Families
Cloudflare is offering Family specific features that automatically filter out bad sites.
Cloudflare for Families will safeguard privacy, and optimize efficiency, but compared to Cloudflare 1.1.1.1; it can block or filter content. The priority here is to protect from security threats and can keep adult content from being accessed by their kids. So it might not be the fastest service to resolve, but it’s going to make sure, bad things stay out of the way.
4] NeuStar Family Secure DNS
It is built for families who do not want children to access mature content, which includes Gambling, Violence, Hate/Discrimination, etc.
- IPv4: 156.154.70.3, 156.154.71.3
- IPv6: 2610:a1:1018::3, 2610:a1:1019::3
5] DNS for Family
DNS for Family is a well-done website offering free DNS IP to configure on the network. They aim to block websites that are considered an adult. The good thing is that they do not block social websites like YouTube, Facebook, and others.
You can use the following DNS servers provided by DNS for Family:
IPv4 DNS Servers:
- 94.130.180.225
- 78.47.64.161
IPv6 DNS servers:
- 2a01:4f8:1c0c:40db::1
- 2a01:4f8:1c17:4df8::1
6] Yandex
Yandex has over 80 DNS servers located in different cities and countries. The company is well known for its Antivirus solution, and it uses its experience to filter out those websites. It offers three types of DNS
Basic, Quick and reliable DNS
- 77.88.8.8
- 77.88.8.1
Safe DNS which offers protection from virus and fraudulent content
- 77.88.8.88
- 77.88.8.2
Family DNS which filters out all adult content
- 77.88.8.7
- 77.88.8.3
We hope the services were easy to configure on your router or computer, and you were able to block access to adult websites and keep your kids away from them.
TIP: You can also use freeware DNS Angel to lock unsafe websites & inappropriate content
DNS не является частным (без DoH)
DNS был разработан почти 40 лет назад, и с тех пор не претерпел значительных изменений. Он полностью незашифрован. Это означает, что он предлагает такой же уровень защиты от любопытных третьих лиц, что и незащищенный HTTP-трафик, что совсем немного. Даже если вы используете HTTPS, любая третья сторона в середине вашего трафика может видеть веб-сайты, к которым вы подключаетесь (но не содержимое вашего посещения). Например, в общедоступной сети Wi-Fi оператор этой сети может отслеживать, какие веб-сайты вы посещаете.
Решение этой проблемы
DNS через HTTPS (DoH
). Этот новый протокол просто шифрует содержимое DNS-запроса, чтобы третьи лица не могли его обнаружить. Основные поставщики DNS, такие как Cloudflare, OpenDNS и Google Public DNS, уже поддерживают его. Однако Chrome и Firefox также находятся в процессе его развертывания.
Помимо улучшений конфиденциальности, DoH предотвращает любое вмешательство в транзитные DNS-запросы. Это просто более безопасный протокол, и каждый должен его использовать.
Однако, даже если вы включите DoH в своем браузере, поставщик DNS должен его реализовать. Большинство подключений к домашней сети по умолчанию настроены на использование DNS-серверов интернет-провайдера, которые, вероятно, не поддерживают DoH. Если вы не меняли его вручную, вероятно, это касается вашего браузера и операционной системы.
Однако есть и исключения. В США.,
Mozilla Firefox автоматически включает DNS через HTTPS
и с использованием DNS-серверов Cloudflare. DNS-серверы Comcast поддерживают DoH и работают
с Google Chrome
а также
Microsoft Edge
.
Однако, как правило, единственный способ действительно получить DoH — использовать другую службу DNS.
СВЯЗАННЫЕ С:
Как DNS через HTTPS (DoH) повысит конфиденциальность в Интернете
Мнения экспертов
По мнению Филиппа Кулина, запретить протокол DNS over TLS теоретически возможно – для этого нужно заблокировать соединения с портом «853». А вот в случае с протоколом DNS over HTTPS трафик данного протокола сложно отличить от стороннего трафика. Решить проблему можно будет лишь блокировкой основных серверов DoH, поддерживаемых , Cisco и CloudFlare.
Дмитрий Артимович полагает, что запрет DoT может реализовать только интеллектуальный фаервол, который сможет отличать обычный запрос к DNS от шифрованного. Аналогичная история и с запретом ESNI. Но если блокировка ESNI будет налажена, это приведет к недоступности большого числа сайтов.
Сервис определения утечки DNS от Whoer.net
Еще одной проблемой является отсутствие защиты данных при передаче запроса на DNS-серверы. DNS-трафик не шифруется, а значит кто угодно имеет возможность посмотреть откуда и к какому сайту был отправлен запрос. При использовании публичных незащищенных DNS-серверов, кто угодно может перехватить передаваемую на них информацию, а так же подменить url и отправить пользователя на фишинговый сайт. Кроме того, информация с публичных серверов нередко собирается и перепродается.
Тест утечки DNS от Whoer.net наглядно показывает используемые DNS-серверы и наличие уязвимости.
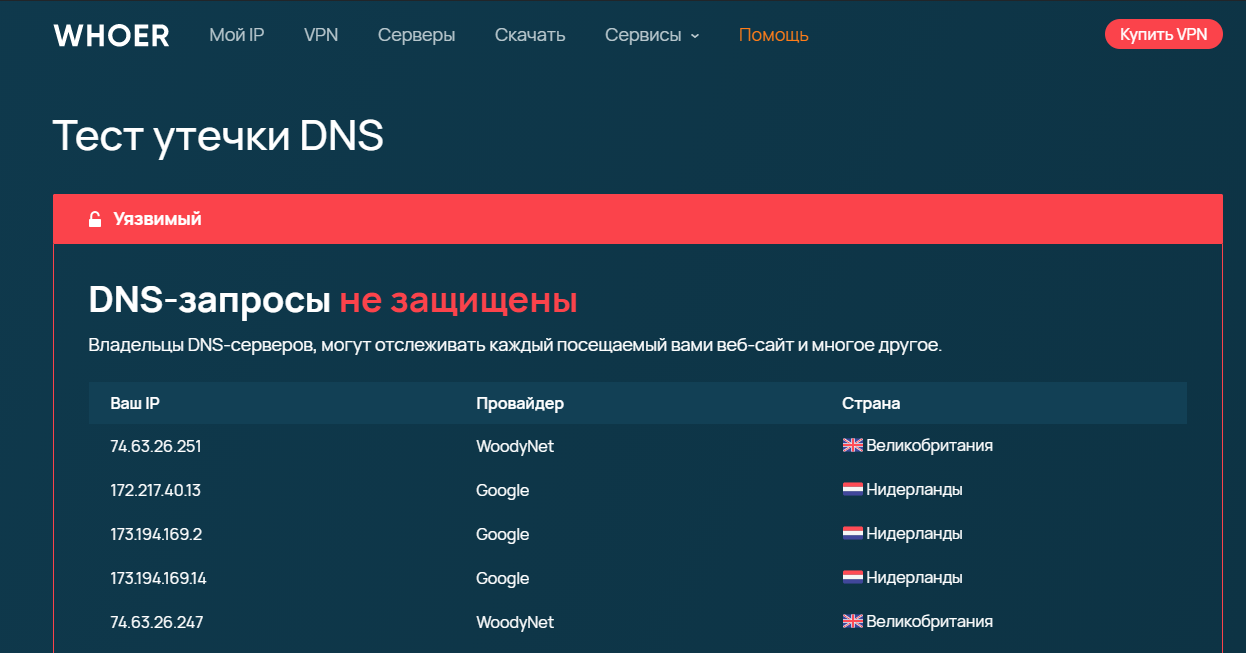
Что делать, если утечка обнаружена и вы хотите устранить уязвимость? Вы можете использовать надежный VPN-сервис с защищенными серверами.
Как включить DNS через HTTPS (DoH)
Если вы хотите включить DoH в своем браузере, вы можете сделать это в Chrome, Firefox и Microsoft Edge.
В Chrome перейдите на страницу chrome: // flags / # dns-over-https, а затем выберите «Включено» в раскрывающемся меню. Перезапустите Chrome, чтобы изменения вступили в силу.
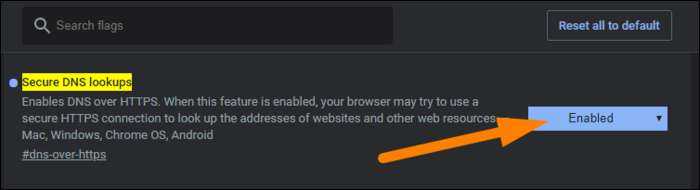
В Firefox эта опция немного похоронена. Откройте меню и выберите Параметры> Общие. Прокрутите вниз и нажмите «Настройки» внизу. Установите флажок рядом с параметром «Включить DNS через HTTPS». Вы также можете выбрать поставщика DNS здесь вручную, если хотите.

СВЯЗАННЫЕ С:
Как включить DNS через HTTPS в Google Chrome
Step 10: Conclusion
So there you have it!
Hopefully this article will have given you some idea of what DNS filtering is, and more importantly how it can be used to help reduce the amount of undesirable web content that your kids can access (either accidentally or deliberately). There are admittedly commercial “black boxes” available that you just plug into your router which provides a content filtered wifi hotspot plus other parental controls. The joy of DNS filtering is that it can be implemented relatively easily, requires no further input once it has been implemented, and best of all is free of charge. As there are some limitations with it then you should probably only regard it as a first line of defence, rather than being the ultimate solution to protecting your kids online.
Please note that the information in the article is based solely on my own limited experience, so I would strongly suggest that you do some research on the topic to confirm for yourself whether anything in this article is true or not! You can get more information on any of the DNS providers from their website.
Finally, it would be remiss of me not to mention the fact that no matter how well you try to shield your kids from the evils of the internet, this is no guarantee that they will not be exposed to undesirable content somewhere outside of your control. No matter what technological solution you may use to help limit their exposure, it is inevitable that they will at some stage see things that you would prefer that they didn’t. In such an instance the only fallback option is to do some old-school parenting. Thankfully there are plenty of resources available on the web to help parents through this process. Sites such as internetmatters.org, betterinternetforkids.eu or webwise.ie have a range of resources to help guide parents on how best to do this.
Good luck!
Add TipAsk QuestionDownload
Почему надо запрещать новые протоколы шифрования
Согласно пояснительной записке к законопроекту, возрастает число случаев использования маскирующих протоколов, позволяющих скрыть фактические сетевые адреса устройств от внешних систем и протоколов шифрования. «Все большее распространение получают протоколы с применением криптографических алгоритмов и методов шифрования TLS 1.3, ESNI, DoH (DNS поверх HTTPS), DoT (DNS поверх TLS)», — утверждают авторы документа.
Олег Иванов, замглавы Минцифры, куратор телеком-отрасли, куратор федпроекта «Информационная безопасность» нацпрограммы «Цифровая экономика»
«Применение указанных алгоритмов и методов шифрования способно снизить эффективность использования существующих систем фильтрации, что, в свою очередь, значительно затруднит выявление ресурсов в сети интернет, содержащих информацию, распространение которой в России ограничено или запрещено», — отмечается в пояснительной записке.
При этом в Едином реестре российских программ для ЭВМ и баз данных содержатся сведения о протоколах с применением криптографических алгоритмов и методов шифрования, возможных к использованию в соответствии с законодательством России.
Dynamic IP addresses
If you are using OpenDNS FamilyShield, you don’t need to bother with this section-you are done for now.
Unfortunately, if you are like most home users, the IP address of your Wifi router could change anytime, though it typically happens once every few days. This happens because most ISPs have a limited number of public IP addresses and keep allocating these to their home users on a need to use basis. What this means is that you need to constantly keep OpenDNS updated about about your Wifi Router’s IP address. To do this, you need to first enable “Dynamic IP Update” from the advanced settings section of the settings tab on your OpenDNS dashboard. You will then need to run a program on a computer on your network that will connect to OpenDNS and keep it updated about your Wifi Router’s IP address. You can download a free OpenDNS Dynamic IP updater application from http://www.opendns.com/support/dynamic_ip/ for Windows or MacOS.
The important thing is this program must be always running on your computer because your Wifi Router’s IP address could change without notice. So you have to set it to be part of your startup applications on your computer (programs that are automatically started when your computer boots up). You can take your local techie’s help on how to do this. Ideally this computer should be running all the time so that your network is always protected.
Some Wifi Routers support this dynamic updating directly in the router, so you don’t need an always-on computer to be running the Dynamic IP updater. Some new models of Netgear and D-Link support OpenDNS. For the truly adventurous, it is possible to write small programs on routers running Linux or an open source software called DD-WRT or Tomato to directly update OpenDNS with the dynamic IP addresses. That, however is a topic for another time.
Gotchas
Like all security solutions — there are important tradeoffs to be made between freedom/usability and protection. No system is fool proof, far from it. What is important is to know the tradeoffs involved and adjust one’s behaviour and expectations accordingly. OpenDNS is one of many solutions available and is a starting point to gaining control over what goes on in your home network. It is not a substitute for good parenting and common sense. You will not achieve 100% control and neither is it desirable – after all you cannot follow your kids into the wider world over which you have no control. It is likely that a determined kid will work his or her way around your firewall. The idea is to let them know what is and what isn’t desirable and to protect younger kids from accidental exposure to the bad stuff. I’m going to list down here a few ways where the OpenDNS system is vulnerable so you are aware.
- Use of device specific DNS. The default behaviour of most internet connected devices like laptops, desktop computers, iPads, smartphones etc. when connecting to a Wifi network is to send all DNS messages to the Wifi Router in your home. However, most users can also modify the settings on their device to bypass the Wifi Router and send DNS messages directly to some publicly available DNS services such as those provided by Google at 8.8.8.8. Kids over the age of 11 should be able to figure this out if they are looking to do so. The way to protect against this is to block port 53 on your Wifi Router. See the following article on OpenDNS.
- Use of VPN services. A user on your network can create a virtual connection (VPN) directly to a server on a remote network and acquire a public IP address from there, bypassing your local router. There are commonly available VPN services like Hotspot Shield and HideMyAss but most require payment with a credit card or through Paypal. OpenDNS can also block these sites to some extent, though there are always methods to get around them. VPN services have legitimate uses, such as allowing people in countries with government run political firewalls (such as China) to access otherwise unavailable web sites.
- Connecting via the 3G or cellular network. Most smartphones today have 3G access as well as a “hotspot” mode that allows them to share their internet access with other devices. So a user in your home could connect his or her computer to the internet over the 3G connection on a smartphone, bypassing your home wifi router. There is not much you can do about this except to keep an eye on the 3G bill!
- Proxying by your ISP. You ISP may be routing all your internet traffic through a proxy, or forcing all your DNS messages to be redirected to their DNS servers. This is not so common, but can happen. You will need to need to speak to your ISP about it – if this happens my recommendation is to switch to a different ISP! I wouldn’t put up with a service where the ISP controls how I connect to the internet.
Norton ConnectSafe
199.85.126.30 / 199.85.127.30
Norton ConnectSafe is a free service that provides a first layer of defense by blocking unsafe sites automatically. On a computer, Norton ConnectSafe does not replace the comprehensive protection of a full security product such as Norton Internet Security or Norton 360.
Instead, Norton ConnectSafe provides basic browsing protection and content filtering for all Web-enabled devices on your home network. Blocks Unwanted Content – Norton ConnectSafe helps keep your kids safe from Web sites with undesirable content. Norton ConnectSafe blocks inappropriate content in 23 different languages.
Step 5: Changing DNS Settings for Cellular Networks on Android and Apple Mobile Devices
Neither Apple nor Android devices allows users to directly change the DNS settings for cellular networks, so a different approach is required. This can be done by downloading and installing a DNS changing app which is then configured to use the CleanBrowsing DNS servers. These apps have the added advantage that they work with both cellular and wifi networks, so you do not need to configure them separately. In addition the settings are automatically applied to new wifi networks, thus overcoming the limitation mentioned previously.
A. Apple:
There are several DNS changing apps in the App store, including the CleanBrowsing.org DNS app. This free app provides the exact same filtering service as outlined previously, and is compatible with devices running iOS 10 or later. The app can be downloaded from the Apple App Store. More information can be found on the CleanBrowsing website.
B. Android:
There are a wide variety of DNS changing apps in the Google Play Store, such as DNSChanger for IPv4/IPv6 from Frostnerd. The app is simple to use, and has an added advantage in that it doesn’t show ads. Once the app is installed you simply click on the Default DNS Addresses bar and then select the DNS service that you require (there are a variety of DNS servers available, including two of the free CleanBrowsing servers).
When you first start a DNS changing app you will be greeted with a connection request screen explaining that the app wants to set up a VPN network on your device. Click on OK to allow the VPN to be set up, and the app will then launch. Once the service is up and running a small key icon will appear at the top of the screen to show that the VPN is active (it can be seen in the upper left corners of the screenshots in Fig. 4). This VPN symbol also provides a visual clue that the DNS filtering is currently active. Irrespective of which app you use, the DNS settings are automatically applied to cellular networks and to existing and new wifi networks.




























